人工光合成・生物電気化学
人工光合成・生物電気化学反応による環境に優しい有価物合成システムの開発
本研究の背景と目的
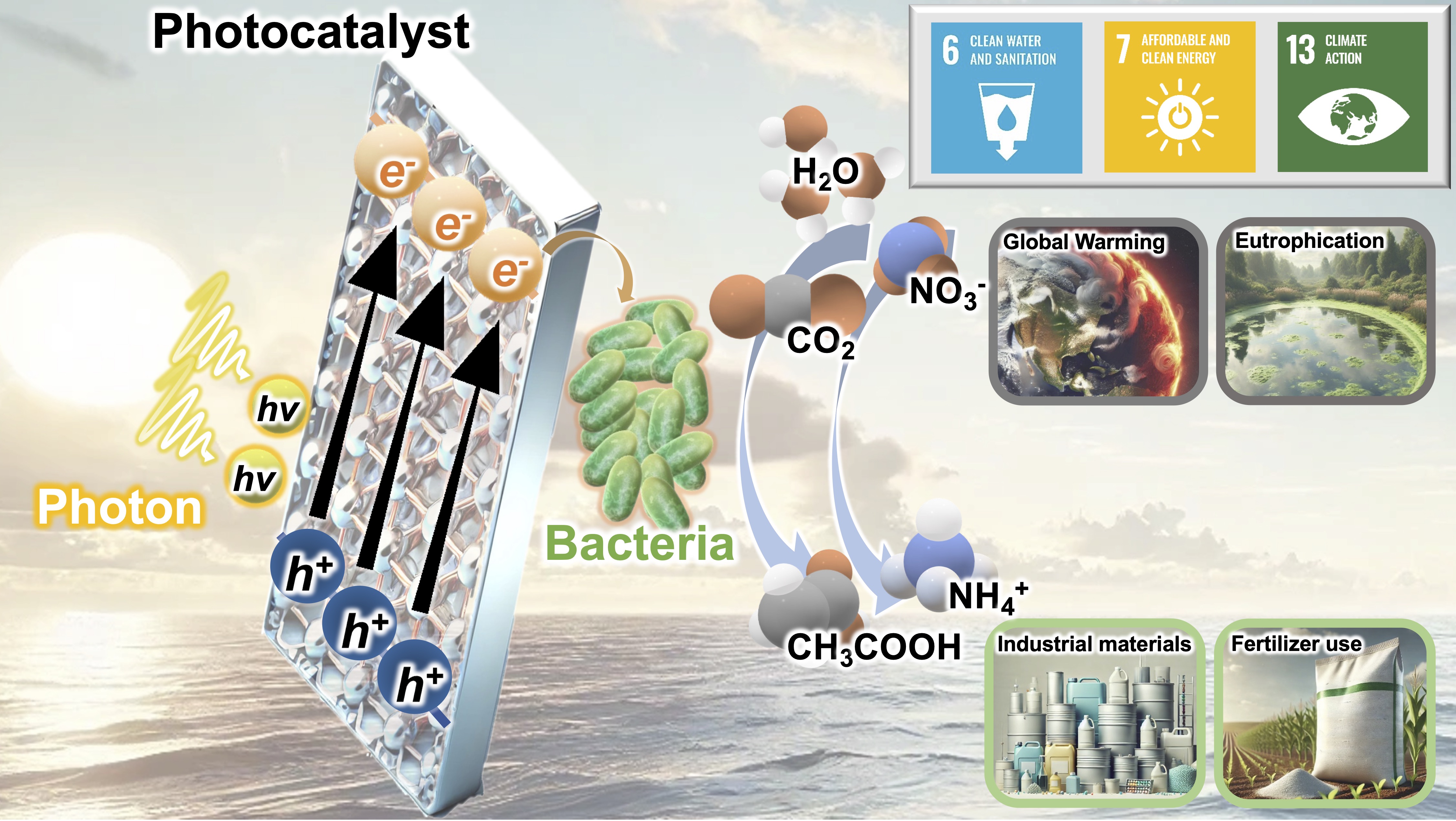
私たちの研究室では、地球上で無尽蔵に利用できる太陽光などの再生可能エネルギーや下水中の有機物(廃棄物)を駆動力として、CO2や窒素化合物(NOx-)などの温室効果ガスを有価物に変換する人工光合成や生物電気化学プロセスに関する研究に取り組んでいます。人工光合成とは、太陽光や水を使って水素ガスや二酸化炭素還元物(メタンなど)、窒素還元物(アンモニアなど)といった燃料や化学物質を生成する技術です。しかし、金属触媒を使用して二酸化炭素や窒素を還元する際には、生成物の選択性が低く、エネルギーの消費が課題となっています。そこで、微生物の持つ酵素の高い選択性を活かした「半人工光合成」に注目が集まっています。この方法では、より効率的かつ環境に優しい形で有価物を合成できる可能性があります。一方、生物電気化学プロセスは、微生物が持つ自然の代謝機能を電気的に制御することで、合成触媒では従来達成が困難であったCO2還元などの反応を行うもので、これらの技術は、再生可能エネルギーの有効利用や資源循環の観点から、特に近年の環境問題の解決に向けた重要な研究分野として注目されています。
本研究では新たな人工光合成・生物電気化学プロセスを開発し、CO2を基質とするC2化合物の合成、NOx-からのアンモニア(NH3)/ヒドラジン(N2H4)合成を達成することを目指しています。これらの技術は、エネルギーや資源の有効利用を図り、温室効果ガス削減に大きく貢献する可能性を秘めています。
論文情報 (詳細は業績をご覧ください)
Matsuo R, Watanabe S, Okabe S.
Chemical Engineering Journal, 2025 505:159093.
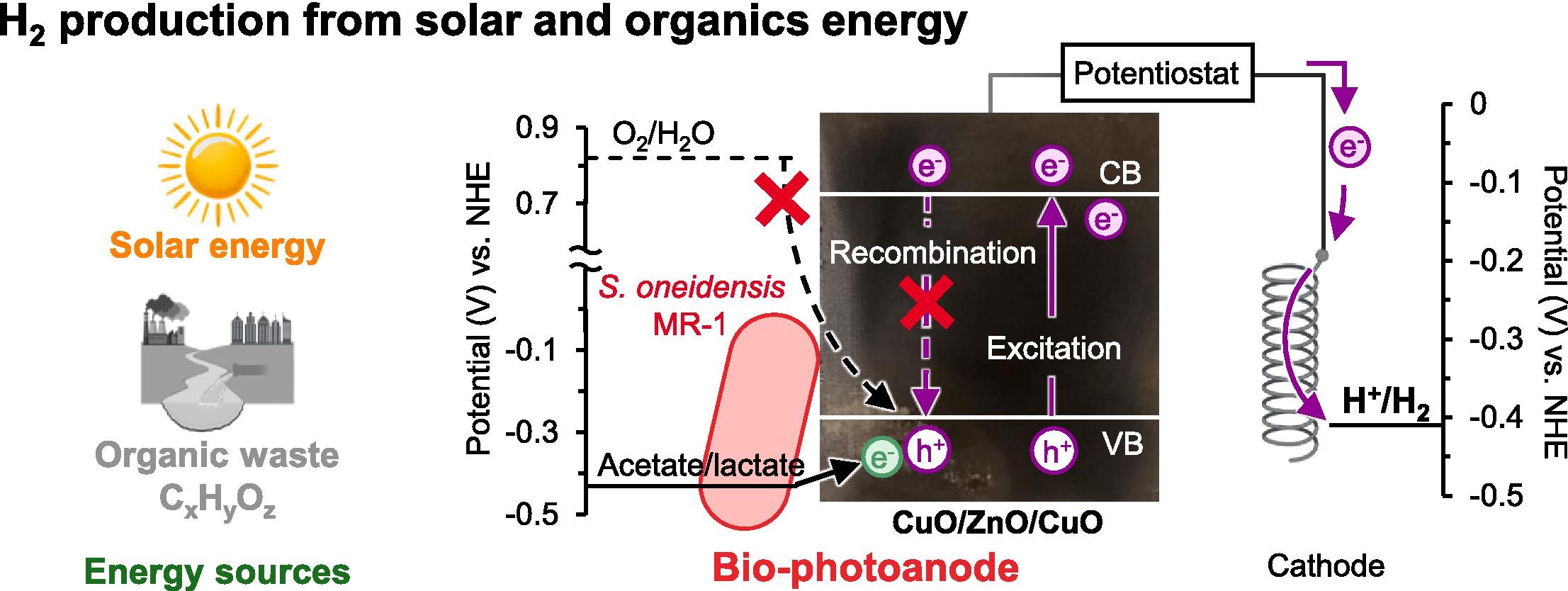
再生可能エネルギーを活用した環境に優しいエネルギーの確保はカーボンニュートラルの実現に向けた重要な課題です。特に、水素は燃焼しても二酸化炭素を排出しないクリーンなエネルギー源であり、太陽光エネルギーを使って効率よく水素を作り出す技術が、持続可能な社会の実現に欠かせない鍵となっています。
本研究では、ナノ構造を持つ光電極CuO/ZnO/CuOと微生物Shewanella oneidensis MR-1を組み合わせた微生物光電気化学セル(M-PEC)を開発しました。このM-PECは、太陽光を活用して従来の6倍の効率で水素を生成することに成功し、光電極CuO/ZnO/CuOは簡易な焼成技術で作製できるにもかかわらず、高い光吸収特性と安定性を実現しました。Shewanella oneidensis MR-1と組み合わせることで高い水素生成性能を達成しました。本研究の成果は、環境に優しく持続可能なエネルギー生産の実現に向けた新たな可能性を提供するものです。
より詳細な情報は以下のページをご覧下さい
Article page
Matsuo R, Takahashi Y, Watanabe S, Okabe S.
Applied Catalysis B: Environmental. 2023 339:123097.
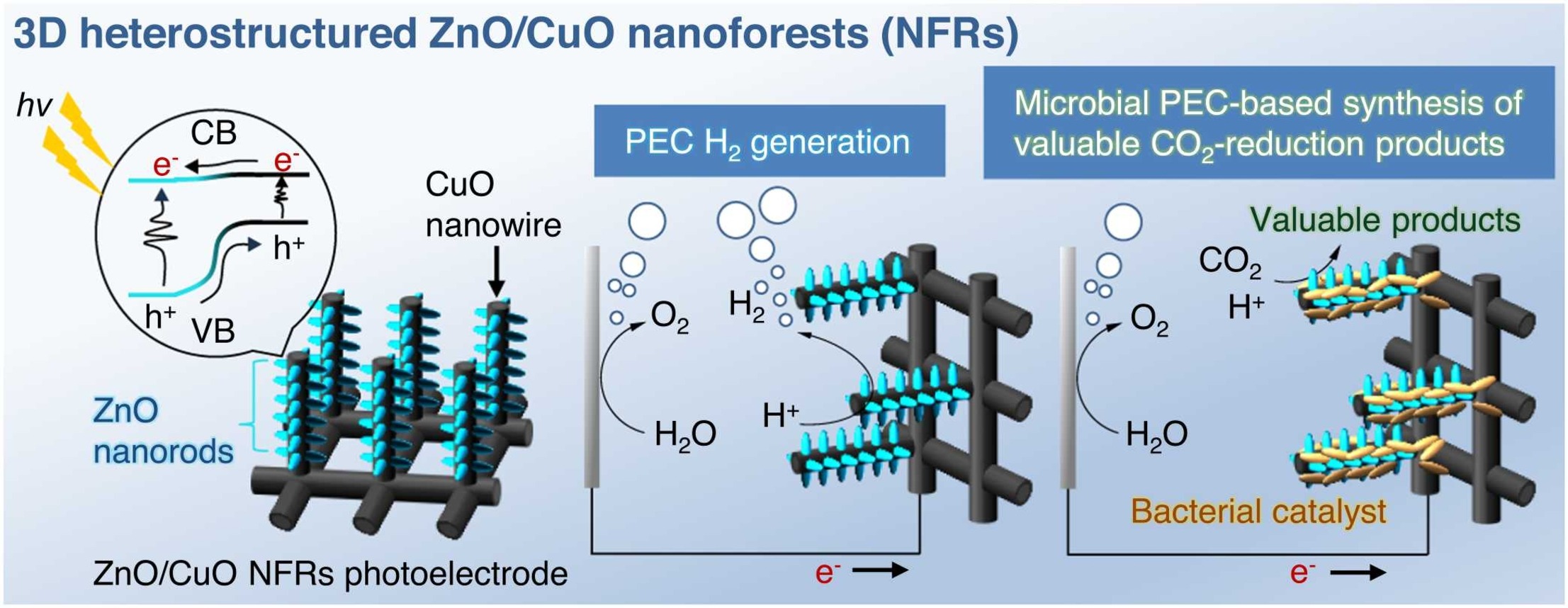
水素生成やCO2還元といったプロセスの効率化は、気候変動対策とエネルギー供給の多様化が求められる中で、再生可能エネルギーを活用したクリーンなエネルギー源の確保とカーボンニュートラルの実現に向けた重要な課題です。特に、水素は二酸化炭素を排出しない燃料として注目されており、また、CO2を化学燃料や製品に変換するCO2還元技術は持続可能な社会に向けた鍵となっています。
本研究では、これらのプロセスを促進するために、3次元ZnO/CuOナノフォレスト(NFRs)を新たに開発し、その光電気化学(PEC)特性と微生物光電気化学セル(MPEC)への応用可能性を評価しました。本研究では、環境に優しい「ガルバニック水中結晶化光合成法(G-SPSC)」を用い、常温・常圧下で純水中でのUV照射によりZnO/CuO NFRsを合成しました。結果として、ZnO/CuO NFRsは優れた光吸収性、大きな比表面積、低い電荷再結合率を示し、0 V vs RHEで2.9 ± 1.3 mA/cm2の高いPEC電流密度と0.63 ± 0.29 µmol/cm2/日の水素生成率を達成しました。また、Escherichia coliに対する生体適合性を評価した結果、Cu2+の溶出による細菌の成長抑制が確認されましたが、0.01 V vs RHEの電位を保持することでCu溶出を防ぎ、成長抑制が解消されることがわかりました。この研究は、環境に優しく高効率な光電極の開発に向けた重要な知見を提供し、今後のエネルギー変換技術や排水処理の効率化において有用な情報となります。
より詳細な情報は以下のページをご覧下さい
Article page


