Studies on ion diffusion in cement-based materials using X-ray microtomography, 3D image analysis, and SiTraM model
| Tel: +81-(0)11-706-6180 |
 Researcher:
Researcher:
 Michael A. Promentilla
Michael A. Promentilla

Research Theme
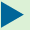
In this study, the 3D micro-geometry pertaining to pore structure characteristics and transport properties is examined from X-ray microtomographic images. This information coupled with SiTraM model is then employed to evaluate the diffusion of ions in cement-based materials.
Research Summary
Background
For a particular post-construction use of cement-based materials, durability performance must be assessed as it can be subjected to aggressive actions during the lifetime of the structure. For example, cement-based materials may be used for marine facilities and underground structures as protective barrier to contain long-lived nuclear waste. Chemical conditions in host formation and low ionic concentration of seawater and underground water impose a high concentration gradient which leads to the diffusion of ions contained in the concrete pore solution to these aggressive solutions. This causes decalcification and dissolution of cement paste hydrates leading to the deterioration of the structure. In the case of chloride ions present in aggressive solutions, they will penetrate into pore solution of concrete.
It is therefore imperative to understand the pore structure characteristics of cementitious materials and model the transport and interaction of ions in this cement-based system. X-ray microtomography and image analysis are employed to visualize the 3D micro-geometry and measure the pertinent pore structure parameters. SiTraM model is then applied to simulate the simultaneous transport of ions in a cement based system since it incorporates the following mechanisms: 1) ions interaction in a multicomponent system, 2) pore structure characteristic of cement-based system , and 3) the ions-solid interaction in cement based system.
Research Strategy