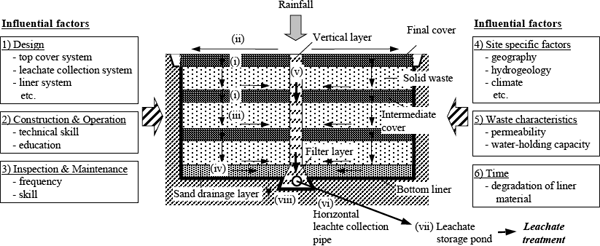
To be environmentally accepted, landfill should be designed and constructed to minimize the short-term and long-term risk. In the past, various risk assessment tools have been proposed. However, most works are carried out assuming specific conditions. Risk from landfill depends on various factors including
- Design: liner system, leachate collection system, top cover system etc.
- Construction & operation: technical skill, education
- Inspection & maintenance: frequency, skill
- Site specific factors: geography, hydrogeology, climate (rainfall, temperature) etc.
- Waste characteristics: Organics, heavy metals, salts; permeability; water-holding capacity
- Time: degradation of liner material
We developed a moisture flow model including these factors and assessed the influence of the factors on leakage of leachate through the bottom liner. As a result, optimal design and operation can be found for a site-specific condition of a landfill at reasonable cost. It will also provide scientific information for risk communication between planner and citizens.
Moisture flow in a landfill is schematically shown in Figure 1. The moisture flow consists of (i) flow in final and intermediate cover, (ii) surface flow, (iii) flow in solid waste, (iv) flow in the sand drainage layer, (v) flow in the vertical layer and the filter layer, (vi) flow in the horizontal leachate collection pipe, (vii) flow in the leachate intake equipment and leachate storage pond, and (viii) flow through the bottom liner. For (i) to (v), Tojo et al. (2002) propose models of moisture flow based on experimental results and theoretical principles. We used those models. For (vi) to (viii), models were developed by the authors. In order to select the important factors for the decrease of leakage rate through the bottom liner, a sensitivity analysis was carried out by changing alternative options for each factor mentioned above.